
The best part a science fiction movie is its futuristic gadgets, and out of the world science-y stuff. Some of them mesmerize us, while others make us cringe in horror. Whatever the reaction may be, they are still interesting. Since we don’t have to deal with the repercussion as they’re hypothetical and not real. Maybe not so much. With the technology advancing with the speed of light, certain things that we’ve only seen in movies till now, are going to become our reality. Here’s a list of some of them- whether good or bad, you decide.
10. Self-Driving Cars
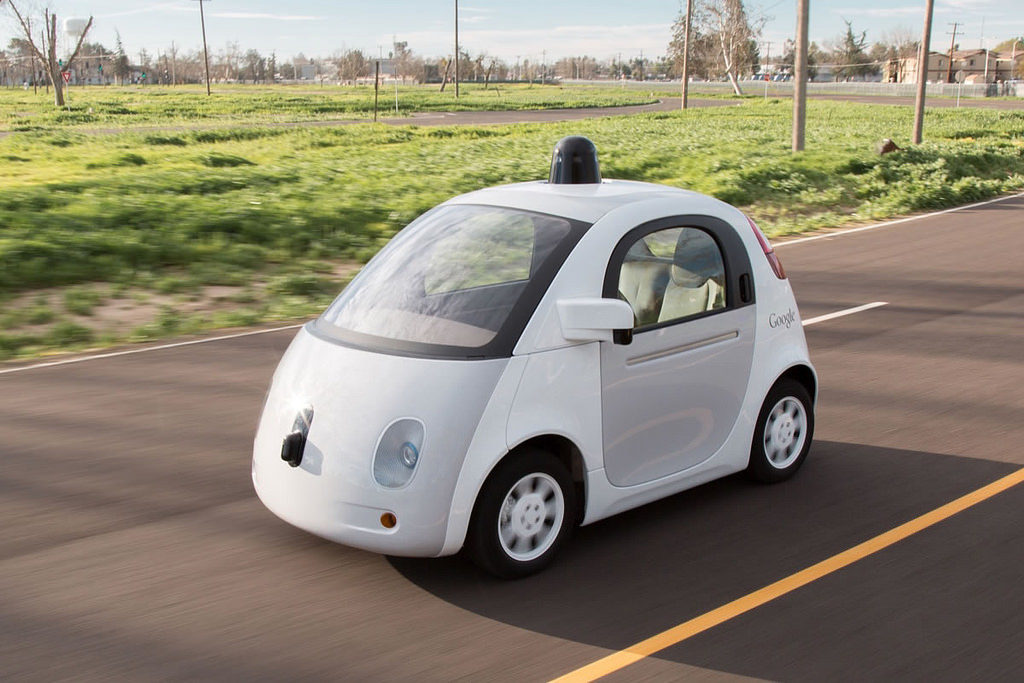

Self-driving cars may soon be cruising the U.S.’ roadways, just like in I, Robot. Federal and state authorities are rushing to keep up with this rapidly advancing technology. The U.S. Department of Transportation just issued its first guidelines for highly automated vehicles or HAVs and fully driver-less vehicles. They could be operating on California roads by the end of the year.
However, Automotive manufacturers are promising commercially available vehicles as early as 2021- four years away. The future vision of this technology is that owning a personal vehicle will be a thing of the past. Services like Uber would have a large fleet of self-driving vehicles. And with our phone we could call on a vehicle. Within minutes the car would be there to pick us up and drive us to our destination.
9. Giant Ship-worm
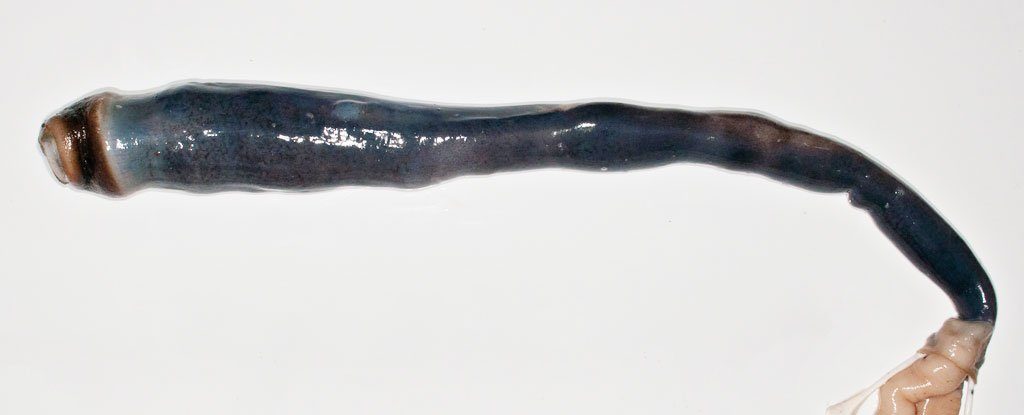

People have known about the existence of this creature for about 300 years. Kuphus polythalamia has a three-to five-foot long, tusk-like shells that encase the animal. They were first documented in the 18th century. They look like an alien creature from a science fiction,. “The shells are fairly common,” begins lead investigator Daniel Distel “But we have never had access to the animal living inside.”. Daniel has a Ph.D., is a research professor and director of the Ocean Genome Legacy Center at Northeastern University. The odd animal doesn’t seem to eat much, instead it gets its energy from a form of sulfur.
8. Gestural Interface

We have seen this technology only in sci-fi movies like Minority Report. The protagonist, played by Tom Cruise, uses gloves that glow at the fingertips. It gives him the power of virtual manipulation. The light seems to allow him to control the screen as if it were a touchscreen. But he’s touching nothing but air. However, a new study might be bringing this technology closer to reality
A team of researchers from Japan reports this week in Applied Physics Letters, that they have discovered a phenomenon called the photo-dielectric effect. This could lead to laser-controlled touch displays. A number of basic circuit components have been developed beyond their traditional electricity-based designs to instead be controlled with light. Some of them are photo-resistors, photo-diodes, and photo-transistors. However, there isn’t yet a photo-capacitor.”A photo-capacitor provides a novel way for operating electronic devices with light,” said Hiroki Taniguchi of the University of Nagoya in Japan. “It will push the evolution of electronics to next-generation photo-electronics.”
“More research is needed before we’ll see light-controlled screens, but the work is a significant step for the field. Further research will look to enhance the effect even more, minimize any energy dissipation due to a drop of dielectric properties, and optimize the material fabrication process”, Taniguchi said. Further studies may also reveal new materials better suited for other electronics applications.
7. Liquid Breathing
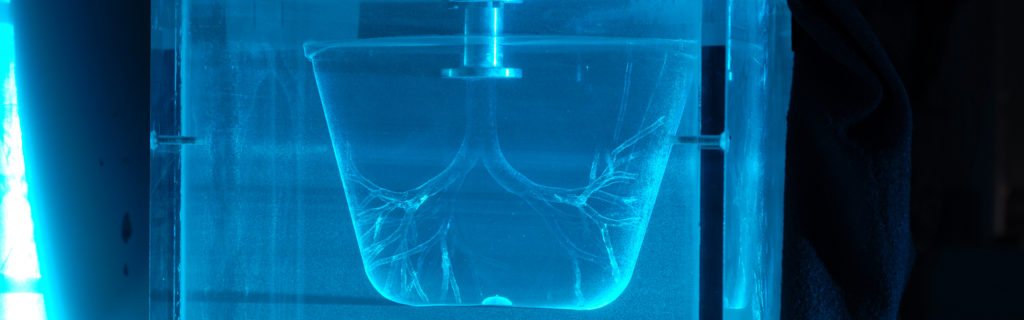
Liquid breathing is no longer a stuff of science fiction. But an imminent reality, thanks to the work of German researchers from TU Bergakademie Freiberg. The lead author of the journal Measurement Science and Technology Mr Janke said: “In clinical liquid ventilation, the lung is filled with liquid, rather than air. The liquid per-fluorocarbon (PFC), which is used for liquid ventilation, has proven perfectly suitable as a breathing medium, as it not only dissolves high amounts of oxygen but also acts as anti-inflammatory for human tissue.”
The researchers used an in-vitro model of the human lung bronchial tree. This was used to measure the effect of oxygen quenching of a fluorescent dye. It has high fluorescence at low oxygen concentrations. Using this technique, they were able to ‘map’ for the first time how the airway absorbed and transported the oxygen, revealing distinctive concentration patterns during inspiration and expiration. Dr Bauer, co-author of the journal said: “Our results showed high potential for this technique to visualize the oxygen transport in a human airway model. We now plan to employ the same technique to look at more complex and realistic human airways.” Very The Abyss-y
6. Time Crystal

Two groups of researchers based at Harvard University and the University of Maryland report March 9 in the journal Nature that they have successfully created time crystals using theories developed at Princeton University. The Harvard-based team included scientists from Princeton who played fundamental roles in working out the theoretical understanding that led to the creation of these exotic crystals.
Time crystals are materials in which atoms and molecules are arranged across space and time.”Our work discovered the essential physics of how time crystals function,” said Shivaji Sondhi, a Princeton professor of physics. “What is more, this discovery builds on a set of developments at Princeton that gets at the issue of how we understand complex systems in and out of equilibrium, which is centrally important to how physicists explain the nature of the everyday world.” This out-of-equilibrium setting has enabled the realization of new and exciting phases of matter, according to Khemani. “The creation of time crystals has allowed us to add an entry into the catalog of possible orders in space-time, previously thought impossible,” Khemani said.
5. Super-laser
In Starwars, a super-laser was a device which merged several separate “super laser beams” into a single exceedingly powerful beam. The largest super-lasers ever designed, were super-weapons capable of obliterating an entire planet with one shot at full power. In a world-leading study researchers at Macquarie University have proven a method for multiplying laser power using diamond. It demonstrates that a laser similar to the Star Wars ‘super-laser’ might become a reality.
“Researchers are developing high power lasers to combat threats to security from the increased proliferation of low-cost drones and missile technology. High power lasers are also needed in space applications including powering space vehicles and tackling the growing space junk problem that threatens satellites,” said co-author of the research, Associate Professor Rich Mildren.
Although other materials have exhibited the same type of beam combining properties, the choice of diamond is essential for high power. The power-transfer effect at the core of the device, called Raman scattering, is particularly strong in diamond. Also, crucially, diamond is outstanding for its ability to rapidly dissipate waste heat.
4. De-extinction

Some types of lost mammals, birds or frogs may soon be able to be revived through de-extinction technologies. The prospect of resurrecting species through cloning or genetic reconstruction through tools such as CRISPR gene-editing has caught the imagination of scientists and the public alike.
The process of de-extinction has become more than a sci-fi concept. In 2003, biologists brought back a Pyrenean ibex. This was done by making a clone of frozen tissues harvested from the last of these goats. The clone died within minutes of its birth due to a lung deformity, but the experiment proved de-extinction was possible .”We can use some of these techniques to actually help endangered species improve their long-term viability,” said ecologist Stanley Temple of the University of Wisconsin-Madison. “Where it gets controversial is when we start talking about species that have been extinct for a very long period of time,” Temple said. Though Critics of de-extinction say reviving extinct animals would do more harm to conservation efforts than good.
3. Self-mutating Organisms
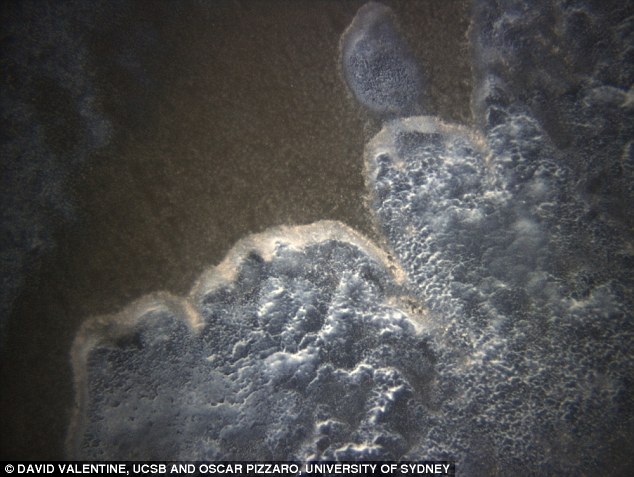
Not fiction, just science- Researchers have discovered a multitude of previously unidentified microorganisms. They possess a genetic element that enables them to self-mutate. “These microorganisms can be 500 times smaller than bacteria like E. Coli,” said UC Santa Barbara microbiologist David Valentine. “They also do unusual things to some of the key genes used for identification, like splitting them into pieces small enough to render them invisible to scientific surveillance. This combined with their ultra-small size explains why they were missed until recently.”
“This discovery reveals how rapid evolution happens in some of Earth’s smallest and most common, yet least-known, microbes,” says Mike Sieracki of National Science Foundation’s Division of Ocean Sciences, and a director for the Dimensions of Biodiversity program, which sponsored the research.
2. Time Travel

Ben Tippett, a mathematics and physics instructor at UBC’s Okanagan campus has created a mathematical model for a viable time machine.”People think of time travel as something as fiction,” says Tippett. “And we tend to think it’s not possible because we don’t actually do it. But, mathematically, it is possible.”
The division of space into three dimensions (x,y,& z) with time in a separate dimension by itself, is incorrect, says Tippett. The four dimensions should be imagined simultaneously, where different directions are connected, as a space-time continuum. Using Einstein’s theory, Tippett says that the curvature of space-time accounts for the curved orbits of the planets. Similarly, time direction of the space-time surface also shows curvature. It is evidenced by the fact that time moves slower, as we move closer to the black hole. His model of time machine uses the curves space-time to “bend time into a circle for the passengers, not in a straight line. That circle takes us back in time.”
Though there is possible to describe this type of time travel in a mathematical equation, but it is not yet possible to make a space-time machine. This is because materials is needed—which call is called exotic matter—to bend space-time in these impossible ways. But they have yet to be discovered. Still, it’s a baby step toward the making of the machine. And who knows, maybe by the next 50 years, we’ll have one.
1. Flying Cars

Who doesn’t want to travel in a Spinner, like those shown in the 1982 classic, Bladerunner. Well your dream might not be too far-off. Two prototypes of ‘flying car’ were launched on 20th April,2017 by the Dutch and Slovak companies,on the French Riviera, at an event showcasing “super-cars” in Monaco. “We are taking reservations from today for deliveries expected in 2020, after the process of (regulatory) approvals is completed,” the Slovak firm’s spokesman Stefan Vadocz told AFP. The Aeromobile vehicle, is a normal four-wheeled car which can unfold its wings to transform itself into a plane able to fly two passengers at a cruising speed of 260 km/h for up to 750 kilometers. The cost? Between 1.2 and 1.5 million euros, depending on options chosen.
However, the Pal-V Liberty, a rival company for the Dutch, is delivering a car-plane more compact, as early as next year, once the official approvals are sealed. It can carry two people for a speed of 160km/h for 400-500 kms. Its is a little cheaper, and its price will be between 299,000 and 499,000 euros. Hmmm. Maybe not so cheap!